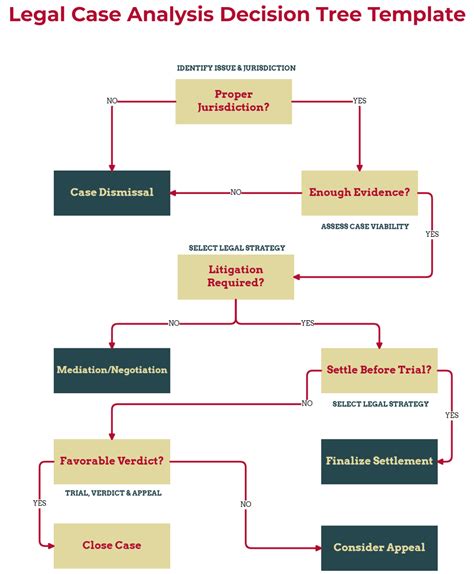
In practice, What Is Anaysis In Court refers to the careful examination of evidence to determine what it proves, how reliable it is, and how the pieces fit together in the legal narrative. Think of analysis as a magnifying glass that helps judges, juries, and lawyers see the details behind the narrative.
This process doesn’t just repeat what’s written in a document; analysis in court interrogates methods, sources, and context to separate fact from inference. A thorough analysis highlights strengths, weak points, and potential bias that could influence outcomes.
Key elements of analytical thinking in court
Analytical work in court evaluates relevance, admissibility, and the chain of custody for physical or digital evidence.
It also emphasizes consistency—whether different pieces of evidence point to the same conclusion—and transparency, so others can follow the reasoning.
Key Points
- Focuses on relevance and credibility of each evidence piece.
- Distinguishes fact from inference and reduces bias in interpretation.
- Follows legal standards for admissibility and method of analysis.
- Often relies on expert testimony to explain technical evidence.
- Strives to present a clear narrative that supports the fact-finder's decision.
Interpreting the process for better understanding
For observers, paying attention to how conclusions are derived helps understand why a judge or jury might accept or reject a piece of evidence.
What is the main purpose of analysis in court?
+The main purpose is to weigh evidence for relevance, credibility, and logical connections, helping the fact-finder separate solid conclusions from assumptions.
Who performs the analysis in a trial?
+Judges, juries, prosecutors, defense attorneys, and often expert witnesses collaborate in the analytical process, each bringing their perspective to evaluate evidence.
How does analysis affect eyewitness testimony?
+Analysis assesses reliability, consistency with other evidence, and potential biases, which can either bolster or cast doubt on eyewitness accounts.
Can analysis in court be challenged or disputed?
+Yes. Analyses can be challenged through cross-examination, objections, and alternative methodologies, ensuring that conclusions meet legal standards.