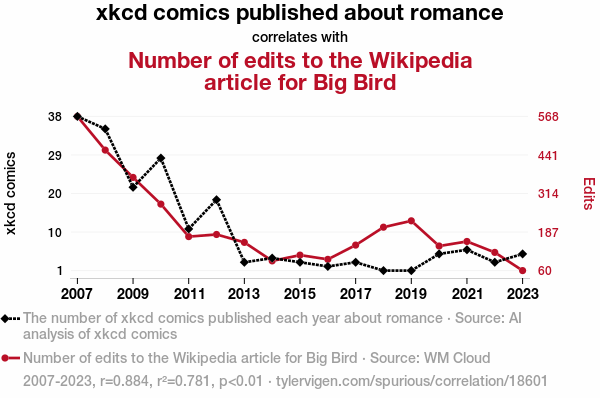
What Is Language Model Spurious Correlation And How To Fix It?
Language Model Spurious Correlation occurs when a language model learns to rely on incidental patterns in data—signals that are correlated with the target outcome but not causally related to language understanding. Recognizing Language Model Spurious Correlation helps teams build more robust systems and avoid overfitting to surface cues during training and evaluation.
Understanding how Language Model Spurious Correlation emerges
In practice, spurious signals come from co-occurrence patterns in data, distribution shifts, and dataset artifacts. Language Model Spurious Correlation can surface when the model picks up on superficial cues like token frequencies, formatting, or topic clusters rather than genuine linguistic generalization. By focusing on surface hints, models may perform well on familiar data but fail under small changes or when prompts differ from training data.
Why Language Model Spurious Correlation matters
As these correlations creep into predictions, users may experience inconsistent outputs, biased choices, or vulnerability to prompt manipulation. Understanding Language Model Spurious Correlation helps guide improvements in reliability, safety, and user trust across applications.
Common sources of spurious signals
Common sources include data sampling biases, annotation artifacts, and evaluation setups that reward memorization over reasoning. When a dataset overrepresents particular phrasing or topics, the model may echo those cues rather than demonstrating true language understanding. This is not about intelligence; it's about shortcuts the model discovers during training.
Impact on performance and safety
Spurious correlations can inflate metrics during validation but degrade real-world performance. They may cause erroneous answers, misclassifications of intent, or unsafe outputs when the model encounters unseen phrasing. Recognizing Language Model Spurious Correlation helps guide robust testing and safer deployments.
Practical fixes to Language Model Spurious Correlation
Fixing spurious signals involves a combination of data, training, and evaluation strategies. Start by diversifying and balancing training data to reduce over-representation of surface cues. Apply debiasing techniques and contrastive objectives to dampen reliance on incidental patterns. Strengthen evaluation with out-of-distribution prompts, counterfactual tests, and causal reasoning checks. Finally, improve transparency through error analysis and clear reporting of what the model actually learned vs. memorized.
Key Points
- Spurious correlations arise from data distribution biases and artifacts, not from true language understanding.
- Evaluating with diverse, out-of-distribution data helps reveal hidden spurious signals.
- Counterfactual prompts and causal testing can separate correlation from causation in predictions.
- Debiasing, data augmentation, and robust training objectives reduce reliance on superficial cues.
- Transparent reporting and thorough error analysis support safer, more reliable models.
What is Language Model Spurious Correlation?
+Language Model Spurious Correlation refers to the model learning to rely on incidental patterns in data that are correlated with outputs but do not reflect true linguistic understanding. These shortcuts can boost apparent performance on familiar data while failing under distribution shifts or with unseen prompts.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I detect spurious correlations in my model?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Use out-of-distribution tests, counterfactual prompts, and ablation studies to see if small changes in input cause large, unexpected output differences. Perform error analysis by inspecting failure modes and checking whether performance relies on surface cues like formatting, vocabulary frequency, or topic clusters.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What practical steps can reduce Language Model Spurious Correlation?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Diversify and balance training data, apply debiasing and contrastive learning, incorporate causal or counterfactual evaluation, and adopt robust prompts. Regularly audit outputs, publish error analyses, and adjust evaluation metrics to penalize reliance on incidental cues.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Is spurious correlation only a problem for language models, or does it affect other NLP tasks?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Spurious correlations can appear in many NLP tasks beyond language modeling, including classification, translation, and question answering. Any task where data patterns are correlated with labels but not causally related can exhibit these pitfalls; robust evaluation and debiasing help across domains.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>